The country reported 299 confirmed COVID-19 cases and six deaths as on 30 June 2020. Despite low numbers of cases, the COVID-19 pandemic has imposed economic and social challenges. The World Bank’s Myanmar Economic Monitor projected a decline in the economic growth from 6.8 percent in FY 2018/19 to 0.5 percent in FY 2019/20. The country faces immense challenges as the clashes between Tatmadaw and Arakan Army continues in Rakhine and Chin States, leading to a large number of displacement of villagers. The country also continues to draw international criticism due to the continued violations of human rights. The month saw positive developments between India and Myanmar in terms of collaboration between women entrepreneurs and increasing trade arrangements. The month also marked the 70th anniversary of China and Myanmar diplomatic relations, but there are reports of increasing discomfort with China’s Belt and Road initiative and illegal supply of weapons from China. The process of planning and formulating the elections has started, and new developments in domestic politics give hopes for change in the country.
COVID-19 and Myanmar’s Response
To further strengthen measures to contain the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Myanmar government announced a 15-day extension of restrictions to be implemented till 15 July. These include a temporary suspension of international flights, a ban on issuing visas and visa-exemption services. The 12-4 a.m. curfew remains in place and all citizens are ordered to practice social distancing.1
Efforts from the side of government have helped enrol about 21 million people to the social transfer programs. Now, around 39% of the population has been covered under the social assistance programs. 2 Individual ministries are announcing relief plans, such as the Ministry of Hotels and Tourism announced a COVID-19 Tourism Relief Plan to help rebuild Myanmar's tourism industry. 3 The Ministry of Social Welfare, Relief and Resettlement (MoSWRR) is providing medical and relief items to the IDP camps in Rakhine and Shan states for prevention of COVID-19 transmission. 4
However, there are shortcomings of the government responses. Given the large proportion of workforce in the informal sector, the Social Security Assistance measures remain exclusionary. The 100 billion Kyat COVID-19 Fund for small businesses, especially SMEs, requires that businesses must repay loans in just one year. SMEs are severely affected by COVID-19, and facing a significant decline in income and it cannot be predicted when businesses will be able to operate normally. 5 COVID-19 has also exposed gender inequalities in the business sector. Women constitute a majority of garment workers, food and accommodation services, many of which already affected by factory closures. Union Minister of MoSWRR joined the virtual ministerial roundtable organised by the UN and shared the measures country has undertaken against prevention of domestic violence, employment opportunities for rural women and the migrant women. 6
Around 80 people illegally entered Maungdaw from refugee camps in Cox’s Bazar from late March to 05 June, according to Maungdaw District Administrative Official- U Soe Aung. Among these, six COVID-19 cases are reported and have raised concerns of spread of the virus. In 2018, the Myanmar government, in an agreement with Bangladesh agreed on the repatriation of Rohingya and opened two reception centres—Taungpyo Letwei and Nga Khura. However, following the spread of COVID-19, Myanmar closed its border entry checkpoints and suspended the repatriation process. 7 Presidential spokesperson- U Zaw Htay stated that security personnel are suspected of helping to transport people who recently entered illegally from Bangladesh. 8 Myanmar is also criticised for taking aggressive measures to contain the spread of COVID-19 virus. Around 8000 people have faced action since late March under the Prevention and Control of Communicable Diseases Law and Natural Disaster Management Law for abusing health care workers, refusing to stay in or fleeing from quarantine centres and organizing religious gatherings and weddings. 9
Myanmar has received immense international support to fight against the COVID-19. To meet the needs of balance of payments, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) approved a disbursement of SDR 86.1 million under the Rapid Credit Facility (RCF) and a purchase of SDR 172.3 million under the Rapid Financing Instrument (RFI). 10 The World Bank approved a $200 million credit to increase agricultural productivity and enhance market access for Myanmar farmers. 11 Similarly, India, China, the Republic of Korea, Singapore and Japan provided Myanmar with the medical supplies in support of fighting against the COVID- 19.
Violence in Rakhine and Chin States Continues
The members of the Northern Alliance comprising of Arakan Army (AA), Ta’ang National Liberation Army (TNLA) and Myanmar National Democratic Alliance Army (MNDAA) called on the Tatmadaw to sign a truce to end the fighting in Rakhine and Chin States. However, the Tatmadaw refused to sign the truce and continued attacks on the members of the AA. Conflicts were reported on 13 June, 22 June, and 29 June. 12 The UN has expressed concern over "reports of intensified fighting" in Rakhine State and has called for "urgent measures to spare civilians" in conflict-affected state. 13
The escalation in fighting has triggered a surge in violence against children and left villagers facing starvation, reported the humanitarian group, Save the Children. Between January and March 2020, in Rakhine State, 18 children were killed, and 71 children were physically injured or maimed. 14 Despite human rights violations reports, the Tatmadaw is implementing its ‘four-cut’ strategy to fight AA, blocking supplies of food and water. This blockage has led to 431 villagers in Rakhine State’s Ann Township displaced during the June month and many more. 15 The Internet shutdown entered the second year in eight Townships of Rakhine and Chin States. On 21 June 2019, Internet shutdown began amid fighting between the Tatmadaw and the AA. Human Rights Watch (HRW) have raised voices that the Internet blockade is keeping villages unaware of the COVID-19 pandemic. 16 Moreover, the police have charged six activists who participated in protests against government-ordered Internet service shutdown. 17 In another set back to the AA, Mandalay District Court proceeded with the lawsuit against alleged members of the AA and three others who were arrested with explosives and arms 10 September 2019. All six are charged under the Counterterrorism Law’s Articles 51 and 52 and face between five years to life in prison. 18
Elections 2020
Myanmar's previous general election was held in November 2015, in which Aung San Suu Kyi-led National League for Democracy (NLD) won and the five-year term is scheduled to end in March 2021. Myanmar's Union Election Commission (UEC) has announced 330 constituencies for the House of Representatives (Lower House), 168 constituencies for the House of Nationalities (Upper House), 644 constituencies for state or region parliaments and 29 constituencies for the ethnic minority in state or region parliaments. There are 97 registered political parties to run campaigns for the elections.
The NLD-candidate, Phyo Min Thein, Chief Minister of Yangon, confirmed that he would not contest in the elections due to his health condition. However, there are differing viewpoints for the reasons. Some suggest that the decision came as he faced criticism for flouting government-ordered restrictions on public gatherings amid the COVID-19 pandemic. In May, Phyo Min Thein attended a Buddhist religious event at the riverside Botahtaung Pagoda in Yangon. The NLD party had also admonished the minister, and Yangon regional lawmakers moved a motion to impeach him. 19
The ethnic parties in Myanmar are also preparing for the election. Except for the Arakan National Party (ANP) and the Shan Nationalities League for Democracy (SNLD), most parties within ethnic groups have merged ahead of the upcoming election. For instance, the Kachin State People’s Party (KSPP) has been formed, in which all six major Kachin parties—have merged. Moreover, the merged parties in Karen, Kachin, Kayah, Mon and Chin states have formed a Coalition Board and announced their solidarity for the election. 20
Finally, for Myanmar’s parliamentary elections, Switzerland has helped to facilitate negotiations on a revised code of conduct. The code of conduct contains rules for peaceful elections and free competition to which parties and election candidates voluntarily commit themselves. Since the end of military rule in 2011, Switzerland supported peace negotiations between the various ethnic groups, the government and the military and has been encouraging the state’s efforts towards democracy. Switzerland will also support the implementation of the code in 2020 elections. 21
International Pressures Continue
The European Union (EU) on 22 June 2020 at the 43rd session of the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) in Geneva placed a draft resolution on “Situation of Human Rights in Myanmar”. The draft resolution was adopted with a vote of two against, eight abstentions and 37 in favour. The Philippines and Venezuela voted against the draft resolution in support of Myanmar. Angola, Cameroon, Democratic Republic of the Congo, India, Indonesia, Japan, Nepal and Senegal voted abstention. Myanmar, however, has rejected the draft resolution and the Permanent Representative of Myanmar- U Kyaw Moe Htun, stated the reasons for the same. He questioned the selective targeting of country-specific resolutions and the use of UN scarce resources for establishing multiple mechanisms to scrutinize a single country. He suggested that the sovereign right of a country should not be intruded Myanmar is undergoing a difficult democratic transition and is facing many challenges, and the issue of Rakhine is just one of many challenges. 22
Myanmar’s has taken initiatives back in the country to challenge the international pressures. On 30 June, three Myanmar military officers were found guilty by a court-martial investigating atrocities against Rohingya Muslims in conflict-ridden Rakhine state. 23 The Central Committee for organizing Union Peace Conference-21st Panglong held a meeting and suggested plans for holding the upcoming peace conference. The Union Ministers of respective committees discussed invitations, accommodation, transportation, security, press and information, healthcare, banking and coordination works for the peace conference. 24
India and Myanmar Engagements
The month saw the collaboration between India and Myanmar to empower women entrepreneurs and generate sustainable livelihoods for women during an online event organised by the FICCI Ladies Organization (FLO). It was organised in partnership with the Indian Embassy in Myanmar, India Myanmar Chamber of Commerce (IMCC) and Myanmar Women Entrepreneurs’ Association (MWEA).The event was an effort to support the Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s Act East policy that focuses on the extended neighbourhood in the Asia-Pacific region. 25
Due to the COVID-19 border restrictions, trade between the two countries-Myanmar and India fell by 40% for the current fiscal year started October 1st, 2019, according to a report by Thura Swiss. According to the agency, the trade value went down from USD 128 million to USD 76 million. On 10 March 2020, the Manipur government on the Indian side decided to close border gates indefinitely at the Tamu (Sagaing Region in Myanmar) and Moreh (Manipur in India) crossing. 26
To ensure that the trade relations grow, in March, the two governments- India and Myanmar- announced plans to import 400,000 tonnes of black gram beans from Myanmar between May 2020 and March 2021. India’s quota on pigeon pea import become effective since 1 April, but they started purchasing them in May-end. According to the notification of India’s Department of Commerce under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, India allowed importing 400,000 tonnes of pigeon peas for the 2020-2021 FY. 27
Due to growing fears of COVID-19, twenty-Eight Civil society organizations and residents in Myanmar’s Sagaing Region- Tamu Township on the Indian border have objected to plans to use a sports hall as a quarantine centre for returnees from India. More than 100 migrants, who have been stranded in Manipur due to COVID-19, are due to return through the Tamu-Moreh border. 28
China-Myanmar Relations
8 June marked the 70th anniversary of diplomatic relations between China and Myanmar. China has provided support, assistance and development to Myanmar and continues this support during the COVID-19 pandemic. China made its fourth donation of medicines, medical and laboratory equipment to the Ministry of Health and Sports. 29
However, the Myanmar government’s discomfort with China is on the rise. After Myanmar’s Auditor General cautioned government officials about continued reliance on Chinese loans, the Myanmar government has formed a tribunal to investigate irregularities surrounding a controversial China-backed city development project near the Thai border in Karen State. The project has been criticised due to lack of transparency, land confiscations, confusion over the scale of construct, and the growing influx of Chinese money as well as suspected illicit activities. 30 Also, the Myanmar government is receiving help from a Swiss company to scrutinize a China-backed study on Beijing’s ambitious railway project to connect Mandalay with Kunming, the capital of Yunnan Province in south western China. 31 Environmental concerns have also been raised with the Shweli River, on the border between Myanmar’s Shan State and China’s Yunnan province, changing its colour around 10 June. Residents suspect the change is due to factories upstream in China dumping waste into the river. The Shweli is a tributary of the Irrawaddy River, the largest river in Myanmar and the source of irrigation for much of the country’s agriculture. 32 The possible pollution raises major questions about environmental regulations and accountability around the BRI projects in Myanmar.
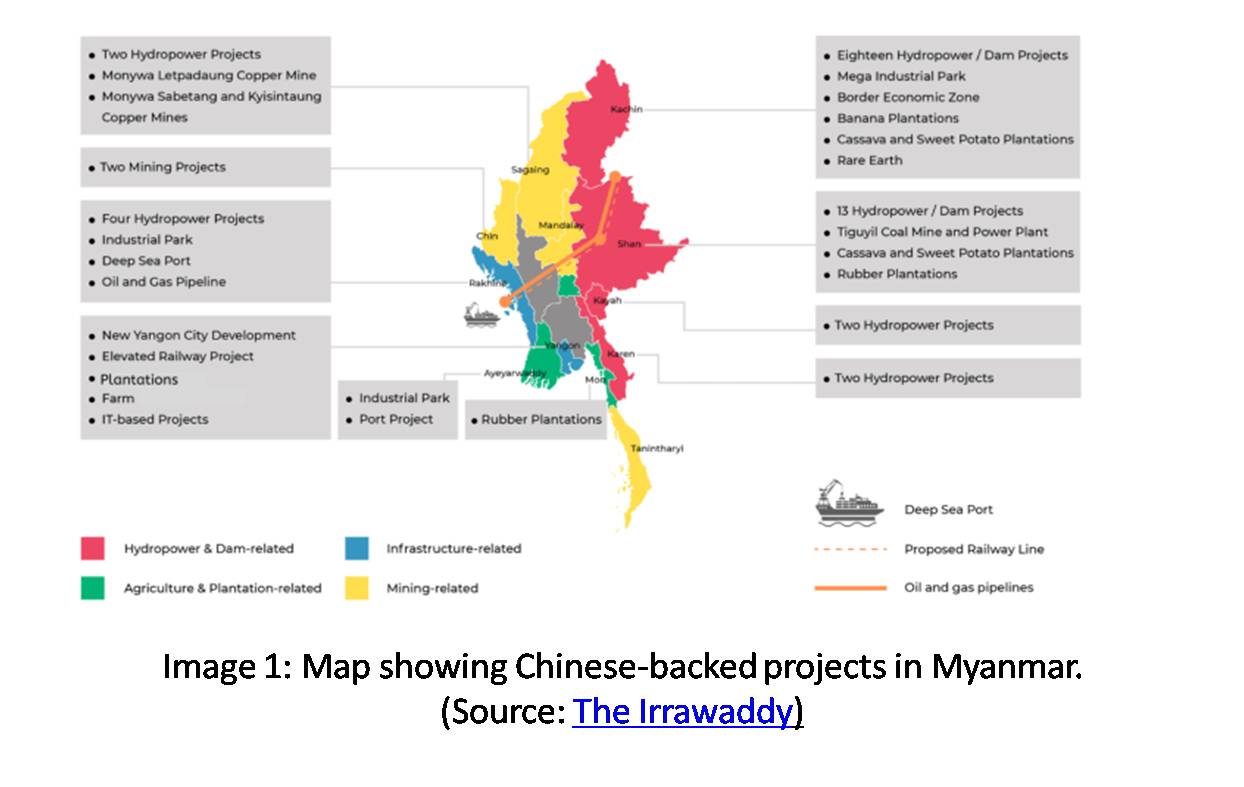
In a significant revelation, Brig Gen Zaw Min Tun, the spokesperson for Tatmadaw reported that a “foreign country” is behind the AA. The Tatmadaw also underlined that most of the seized weapons from an ethnic group called Ta’ang National Liberation Army (TNLA) in November 2019 were all Chinese made. The Executive Director of Myanmar Institute for Peace and Security-U Min Zaw Oo revealed that a majority of the weapons used by Myanmar ethnic armed groups operating near the Chinese border are made in China. 33 Recently, a joint task force, including the Thai military and police, also seized large packages of Chinese-made weapons. 34
Investments in Myanmar
Myanmar finalised its second Investment Policy Review (IPR) with the help of the France-based Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) to identify further policy reforms needed to make the country a more attractive destination for quality, responsible investment for both foreign and local investors. Myanmar conducted its first IPR in 2014, and since the NLD took office in 2016, it has implemented several economic reforms including passing a new Companies Law in 2018 and launching an online company registration system to boost confidence among foreign investors.
However, Myanmar faced significant a decline in foreign investment from USD 9.5 billion in fiscal 2015-16 to USD 5.7 billion in 2017-18 after Western investors turned away from the country due to the Rohingya crisis. Since late 2018, Myanmar has held investment and business forums both abroad and at home, with Japan, South Korea, China, Singapore, the US, UK, and Australia and many others. Recently, Union Minister for Investment and Foreign Economic Relations-U Thaung Tun said Myanmar was on track to meet its FDI target of USD 5.8 billion for this fiscal year based on current data. 35 U Thaung Tun also attended a Special ASEAN Economic Ministers Meeting on COVID-19 and a Special ASEAN Plus Three Economic Ministers Meeting on COVID-19 via videoconference. The meetings culminated in the adoption of the Hanoi Plan of Action on Strengthening ASEAN Economic Cooperation and Supply Chain Connectivity in Response to the COVID-19 Pandemic and an ASEAN Plus Three Economic Ministers’ Joint Statement on Mitigating the Economic Impact of COVID-19. 36
Miscellaneous
The National Planning Commission conducted its first meeting for the year and the Union Ministries and region/state governments successfully submitting the National Plan for 2020-2021. The National Plan has emphasized on development of road and bridge network, electrification, economic recovery in the post-COVID-19 period, support to SMEs and employment opportunities for low-income businesses. During the meeting, the Myanmar President emphasized the government’s policy of ‘No one is left behind’ in striving for economic and sustainable development. 37
Myanmar is also strengthening its ties with Russia as the Myanmar military Chief Senior General-Min Aung Hlaing’s visited Russia to attend the 75th anniversary of Russian Victory Day. According to political analyst and ex-military officer-Dr. Aung Myo, Russia considers Myanmar important to geopolitics because the country borders the Indian Ocean and the Bay of Bengal and is one of Russia’s biggest customers for weapons. As the Western bloc shuns Myanmar from time to time, Russia has sought to become allies with the country. 38
Conclusion
The WHO’s representative of Myanmar- Dr. Stephan Paul Jost stated that “Myanmar has done extraordinarily well so far to contain the COVID-19 spread”. Myanmar must continue to take measures and restrictions to contain the spread of the virus and must simultaneously take efforts gradually open and revive the economy. Myanmar is an agriculture-based country, and it has the potential to fulfil the world's food requirement after COVID-19, according to Union Minister for Investment and Foreign Economic Relation- Thaung Tun. The efforts must be to enhance the exports of agricultural products. India has initiated active trading relations with Myanmar for agricultural products such as vast imports of pulses in the times of COVID. There is also a need to incorporate labour market interventions in terms of skill mapping, matching skills to jobs and promotion of labour market flexibility measures to address the unemployment challenges and revive the economy. The 2020 Elections provide an opportunity to the political parties to reconsider and reorient their policies for the development of the country as a whole. The elections also provide an opportunity to the Tatmadaw to change its ways and declare the ceasefire in the Rakhine and Chin States where the Arakan Army operates. The international pressures and criticisms give a push to the government and the Tatmadaw to initiate talks with all sections of ethnic armed groups so that peace and stability is restored in the country.
- https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2020-06-27/myanmar-extends-travel-ban-curfews-to-contain-covid-19-spread
- http://mizzima.com/article/global-and-myanmar-experiences-social-protection-address-impact-covid-19
- https://www.mmtimes.com/news/myanmar-airways-gears-rebound-tourism.html
- https://www.globalnewlightofmyanmar.com/supplies-reach-idp-camps-in-rakhine-shan-for-measures-against-covid-19/
https://www.globalnewlightofmyanmar.com/moswrr-implement-covid-19-preventive-measures-in-kachin-rakhine/ - https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/burma/myanmar-smes-urge-suu-kyi-ease-covid-19-loan-policies.html
- https://www.globalnewlightofmyanmar.com/union-minister-dr-win-myat-aye-discusses-gender-perspective-for-covid-19-rehabilitation-period/
- https://www.irrawaddy.com/specials/myanmar-covid-19/myanmar-concerns-mount-covid-19-cases-among-illegal-returnees-bangladesh.html
- https://www.eurasiareview.com/21062020-myanmar-security-personnel-complicit-in-illegal-border-crossings/
- https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/burma/8000-citizens-prosecuted-myanmar-covid-19-breaches.html
- https://www.imf.org/en/News/Articles/2020/06/26/pr20247-myanmar-imf-executive-board-approves-a-us-356-5m-disbursement-address-covid19
- http://www.mizzima.com/article/project-boost-agricultural-productivity-support-farmers-myanmar-wake-covid-19
- https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/burma/arakan-army-blamed-ambush-police-trucks-western-myanmar.html
https://www.arakan.news/2020/06/myanmar-army-shot-and-killed-civilian.html - https://www.channelnewsasia.com/news/asia/un-warns-of--intensified-fighting--in-myanmar-s-rakhine-state-12878666
- https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2020/06/children-killed-maimed-myanmar-conflict-200623010811604.html
- https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/burma/hungry-villagers-flee-fighting-myanmars-rakhine.html
- https://www.npr.org/sections/coronavirus-live-updates/2020/06/24/882893419/parts-of-myanmar-unaware-of-covid-19-due-to-internet-ban-advocates-say
- https://www.rfa.org/english/news/myanmar/activists-charged-06242020154538.html
- https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/burma/alleged-arakan-army-members-face-terrorism-prosecution-mandalay.html
- https://www.rfa.org/english/news/myanmar/chief-minister-06152020184934.html/ampRFA?__twitter_impression=true
- https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/myanmars-ethnic-parties-find-strength-unity-prepare-general-election.html
- https://www.swissinfo.ch/eng/switzerland-mediates-in-myanmar-election-process/45865210
- https://www.globalnewlightofmyanmar.com/myanmar-rejects-draft-resolution-tabled-by-eu-at-43rd-session-of-the-human-rights-council/
- https://www.channelnewsasia.com/news/asia/myanmar-finds-soldiers-guilty-in-rohingya-atrocities-court-martial-12886484
- https://www.globalnewlightofmyanmar.com/union-peace-conference-to-be-held-under-covid-19-guidelines/
- http://www.mizzima.com/article/india-and-myanmar-seek-roadmap-help-women-entrepreneurs
- http://mizzima.com/article/myanmar-india-trade-falls-40-due-covid-19-trade-post-closures
- https://www.globalnewlightofmyanmar.com/pigeon-peas-fetch-good-price-as-india-demand-rises/
- https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/burma/india-myanmar-border-town-opposes-quarantine-center-amid-covid-19-fears.html
- https://www.globalnewlightofmyanmar.com/china-makes-fourth-donation-against-covid-19-to-myanmar/
- https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/international/world-news/myanmar-govt-forms-tribunal-to-probe-china-funded-city-project/articleshow/76440927.cms
- https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/burma/myanmar-pulls-swiss-firm-scrutinize-chinas-bri-project.html
- https://www.aseantoday.com/2020/06/a-river-on-the-china-myanmar-border-just-turned-red-what-does-it-mean-for-the-belt-and-road-initiative/
- https://eurasiantimes.com/now-myanmar-accuses-china-for-creating-trouble-in-the-country/
- https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/burma/chinese-made-arms-due-myanmar-seized-thai-border.html
- https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/burma/myanmar-launch-investment-polices-upon-completing-review-oecd.html
- https://www.globalnewlightofmyanmar.com/union-minister-u-thaung-tun-participates-in-special-asean-economic-ministers-meeting-and-asean3-economic-ministers-meeting-on-covid-19-response/
- https://www.globalnewlightofmyanmar.com/president-u-win-myint-presides-over-first-meeting-of-national-planning-commission/
- https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/burma/top-myanmar-generals-visit-to-russia-will-strengthens-ties-myanmar-military.html











Post new comment