The Union Budget for FY 2025-26 reflects the government’s commitment to continuity, incremental reforms, and fiscal prudence. With a focus on tax relief, infrastructure, manufacturing, and technology, the budget aims to drive economic growth while addressing social welfare. While the resources are limited the competing demands on it are not. So as always, while the budget offers several positives, but there are areas that could have been better addressed. Based on the priority given in allocating resources to the various competing demands, below is an analysis of the good, the limited good, and the not so good aspects of the budget, along with an sectoral overview
Key Highlights at a Glance
| The Good | The Limited Good | The Not so Good |
|---|---|---|
| - Major Personal Income Tax Relief | - Limited Focus on Agriculture | - Tax Cuts vs. Fiscal Prudence |
| - Strengthening Manufacturing & Exports | - Falling Rural Employment Spending – Needs more spend | - Feeble Push for MSMEs – backbone of economy and employment generators |
| - Technology & Innovation Boost Strategy to promote leap frog technology | - Healthcare Gaps | - Limited Green Energy Transition – Weak Push for Renewables |
| - Strengthening Manufacturing & Exports | - Falling Rural Employment Spending – Needs more spend | - Feeble Push for MSMEs – backbone of economy and employment generators |
| - Focus on Infrastructure & Urban Development | - Phasing Out of EV Subsidies – industry heavily invested & expects subsidy continuity | |
| - Social Welfare & Financial Inclusion |
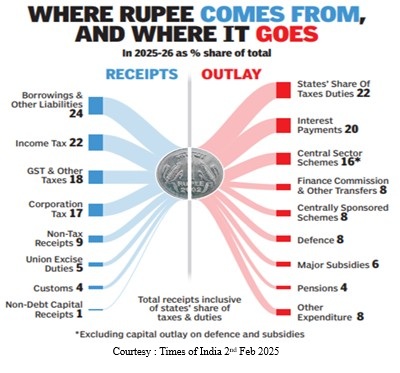
Sectoral Overview
- Agriculture & Rural Development
- Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana for 100 districts.
- Focus on high-yield seeds and sustainable agriculture.
- Rural Prosperity & Resilience Program to promote employment albeit with lower spend.
- Manufacturing & Industry
- PLI scheme extended for auto components and specialty steel.
- Deep-tech fund and ease-of-doing-business reforms for startups.
- Digital Economy & Innovation
- ₹2,000 crore for India AI Mission.
- Bharat Net allocation increased to ₹22,000 crore to improve rural connectivity.
- New mission on geospatial technology for enabling a framework for Global capability centres (GCCs)
- Urban Development & Transport
- ₹1 lakh crore for Urban Challenge Fund.
- ₹25,000 crore Maritime Development Fund.
- Modified UDAN scheme to improve regional air connectivity.
- Financial Services & Investment
- FDI cap in insurance sector removed.
- Expansion of PM SVANidhi and MSME credit schemes.
- Energy & Environment
- National Manufacturing Mission to support clean energy.
- Nuclear Energy Mission to operationalize five small reactors by 2033.
Impact on Different Segments
Impact on Industry
- The emphasis on manufacturing, particularly under the National Manufacturing Mission and PLI schemes, is expected to create a more competitive industrial environment.
- Infrastructure investments, including transport and logistics, will reduce operational costs for businesses.
- Increased FDI flexibility in insurance and regulatory reforms will encourage foreign investments.
Impact on Manufacturing Sector
- Increased budget allocation for industrial goods and MSMEs will support growth and employment in the sector.
- Lower custom duties on imported industrial inputs will enhance competitiveness.
- Focus on sustainable production will help industries transition towards sustainable practices.
- Boost for the automobile sector through PLI schemes and limited EV infrastructure support.
Impact on the Services Sector
- The extension of startup tax benefits and increased support for IT and AI will boost innovation and entrepreneurship.
- Growth in the tourism sector through destination development schemes will support hospitality and related industries.
- The financial sector will benefit from increased investment facilitation and regulatory streamlining, promoting a more business-friendly environment.
- Digital transformation initiatives, including AI, fintech, and research funding, will support the IT and digital services industries.
Impact on the Common Man
- Personal income tax relief will increase disposable income, enhancing consumer spending.
- Investment in urban infrastructure and housing will improve the quality of life in cities.
- Expansion of broadband under BharatNet will provide better access to digital services in rural areas and promote digital inclusion.
- New employment generation schemes will create job opportunities, particularly for youth and marginalized sections.
Conclusion
The Union Budget 2025-26 balances growth with fiscal prudence but leaves gaps in social welfare and sustainability. While tax cuts and infrastructure spending will likely drive short-term gains, long-term success depends on effective implementation of reforms. The push for leapfrogging technology, promoting innovation and infrastructure creation is palpable, and with a stronger push on green energy, MSME support, and rural employment, this budget could have been more inclusive. As India aims for a Viksit Bharat 2047, policy continuity and execution will determine its success.
(The paper is the author’s individual scholastic articulation. The author certifies that the article/paper is original in content, unpublished and it has not been submitted for publication/web upload elsewhere, and that the facts and figures quoted are duly referenced, as needed, and are believed to be correct). (The paper does not necessarily represent the organisational stance... More >>
Image Source: https://www.taxscan.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/Union-Budget-Union-Budget-2025-Union-Budget-2025-Expectations-Everything-We-Know-So-Far-Expectations-taxscan.jpg









Post new comment