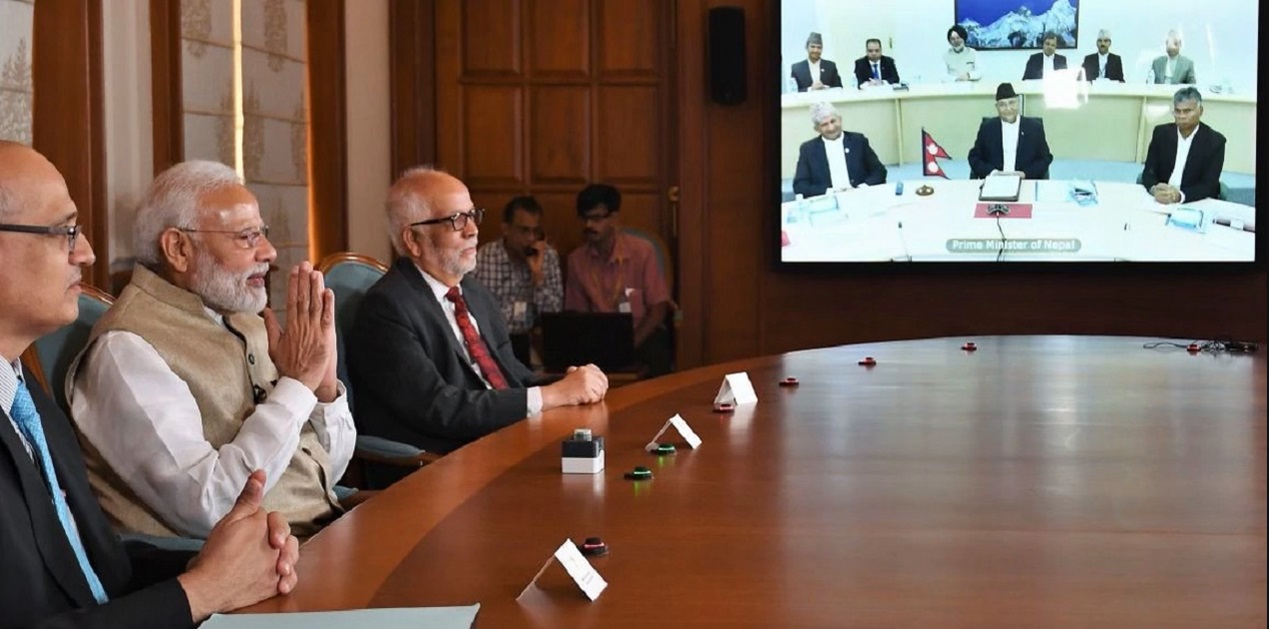
The Mothihari-Amlekhgunj pipeline was jointly inaugurated on 10th September 2019 by Prime Ministers of both nations through a video link. The 69 km pipeline multiproduct pipeline is a government to government (G2G) project. It is built jointly by state-owned Indian Oil Corporation (IOC) and Nepal Oil Corporation (NOC) and can supply petrol, diesel, kerosene and aviation fuel. It will be supplying only diesel in its first phase. The pipeline was constructed in record 15 month’s time. This is the first cross border pipeline in the South Asia region.1 The total cost of the pipeline is INR 3.24 billion. 2 The total capacity of the pipeline is 2 million metric ton per annum. 3
Nepal currently consumes about 2.66 million tonnes of oil and there has been a rise in the per capita consumption of oil in Nepal.4 As per the World Bank (WB), Nepal’s per capita oil consumption has grown from 390.824 kgs in 2011 to 434.449 kgs in 2014 and it is expected to rise in the coming years.5 Keeping its energy needs in mind, Mothihari-Amlekhgunj cross-border pipeline was finalised during PM Modi’s visit to Nepal in 2014. In August 2015 a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed on the pipeline between India and Nepal through Indian Oil Corporation Limited (IOCL) and Nepal Oil Corporation (NOC) in 2015.6 The construction began after the ground-breaking ceremony held in Hyderabad house during PM Oli’s visit to India in April 2015.
The importance of this pipeline for Nepal’s energy security and its impact in strengthening bilateral ties was highlighted by Nepal PM K.P Oli. In his speech, he said that this pipeline will reduce air pollution and the cost of oil transportation. The Nepal Oil Corporation has estimated that this pipeline will help it save INR 2 billion annually which occurred in the freight of petroleum products.7 The benefit of the pipeline was immediately transferred to the people of Nepal and the price of petrol diesel and kerosene was reduced in Nepal was 2 Nepalese Rupee per litre. PM Oli also highlighted how the Indian-aided joint projects have gained momentum in recent years due to the understanding reached between PM Modi and his government.
Nepal is a landlocked country and shares a porous border with India. Due to its geographical limitations, Nepal is dependent on India for trade and transit. This is shown by the fact that India’s share in Nepal’s total trade is 61.2 percent and it accounts for one-third of Nepal’s foreign direct investments (FDI) and 100 percent for its oil supplies.8 India has been supplying oil to Nepal from its seven pick up points (Gauriphanta, Rupaidiha, Siliguri, Sonauli, Raxual, Jogbani and Bhithamore) as per the Supply Contract Agreement between both the countries.
The neighbourhood has been central to Prime Minister Modi’s foreign policy since his first term and he has continued it in his second term. India and Nepal relations has got a new thrust under PM Modi and there have been regular high-level exchanges between the two countries. In the last 18 months both the PMs have met each other four times on different occasions which have expanded the areas of cooperation and led to improvement of bilateral ties. Today New Delhi-Kathmandu cooperation are in various areas such as education, agriculture, connectivity, hydropower, tourism, industries, defence etc. Apart from the 2015 blockade, the relations between both the countries has been on an upswing, wherein India has also contributed for the reconstruction of Nepal after the devastation caused by 2015 Earthquake.
India has always assisted Nepal as per their needs and invested in projects which directly impact the people of Nepal. In the last two years, India has increased its role in the development of Nepal and also diversified its areas of cooperation. India provided with an aid of Rs. 1.6 billion9 for construction of 50,000 houses in Nuwakot and Gorkha district. Further, India also constructed Pashupatinath Dharamshala10 and Integrated Check Post (ICP) at Birgunj. 11 All these projects and assistance will help in boosting interconnectedness and interdependence between both the countries.
The influence of India in the Himalayan state has been challenged by China. It has been investing heavily in Nepal and its total FDI investment in the country is 10,844.10 million Nepalese rupees.12 Nepal is part of China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and also signed the Trade and Transit Agreement (TTA) in September 2018 to give Nepal access to four sea-ports (Tianjin, Shenzhen, Lianyungang and Zhanjiang) and three land ports (Lanzhou, Lhasa and Xigatse) in China.13
There has also been an increase in high-level exchanges between China and Nepal. This year Nepal’s President Mrs. Bidya Devi Bhandari visited China in April to meet President XI Jinping and signed seven bilateral agreements.14 Nepal’s Minister of Foreign Affairs, Pradeep Kumar Gawli also visited China in July.15 During the inauguration of Mothihari-Amlekhgunj pipeline, the Foreign Minister Wang Yi was on a three-day (8th-10th September) visit to Nepal to promote “friendship between two countries”.16 During his visit Wang Yi said that the preparations for Chinese President Xi Jinping had started and he will soon visit Nepal.17
Although China and Nepal are facing difficulties in implementing their bilateral projects. A list of 35 projects was given to China to be developed under BRI during PM Oli’s visit to China in June 2018.18 But after reviewing the projects the Chinese asked Nepal to cut down on the projects and now the projects have been cut down from 35 to 9. 19 The most ambitious project under BRI, the cross border railway project which will connect Kerung city in Tibet to Kathmandu in Nepal has been termed by locals as kagat ko rail (paper railway) and sapna ko rail (dream railway). Nepal’s government announced in its last budget that the construction of this project will commence in two years but has not allocated a budget for a detailed study. 20 There has been growing resentments against the BRI project among civil societies and environmentalists in Nepal.
The friendship between India and Nepal is time-tested friendship and shares lots of commonalities. PM Modi and PM Oli share a great rapport between them and both endorses each other visions for their respective countries. PM Modi has repeatedly supported PM Oli’s vision of ‘Prosperous Nepal and Happy Nepalis’ and PM Oli has backed PM Modi’s ‘Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikaas’. Both the countries have a stable government with an absolute majority in their countries and this can help in building a strong relationship between India and Nepal. Nepal is a new democracy and India is the largest democracy in the world and India can help in the functioning of democracy by sharing its knowledge and expertise related to various aspects of running a democratic country.

India understands that energy security will be very important for its developing neighbours and they will look towards India for its energy security. Indian projects in the neighbourhood have been accused of delivery lag on several occasions. The construction of Motihari-Amlekhgunj pipeline in record time will help in building a positive image about not only in Nepal but in the whole of South-Asia. This pipeline will also open avenues for more pipeline between India and Nepal and between India and its neighbours in the region.
References
- hhttps://www.mea.gov.in/press- releases.htm?dtl/31811/prime+minister+and+kp+sharmaAccessed September, 13, 2019.
- https://www.iocl.com/aboutus/NewsDetail.aspx?NewsID=49404&tID=8, Accessed September, 14, 2019
- https://www.mea.gov.in/press- releases.htm?dtl/31811/prime+minister+and+kp+sharmaAccessed September, 15, 2019.
- https://www.business-standard.com/article/current-affairs/india-and-nepal-open-south-asia-s-first-cross-border-oil-pipeline-119091000557_1.html, Accessed September, 14, 2019
- https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/EG.USE.PCAP.KG.OE?end=2014&locations=NP&name_desc=false&start=2000, Accessed September, 14, 2019
- https://www.iocl.com/aboutus/NewsDetail.aspx?NewsID=49404&tID=8
- https://www.ndtv.com/india-news/prime-minister-narendra-modi-nepal-counterpart-kp-sharma-oli-launch-south-asias-first-cross-border-p-2098498, Accessed September, 13, 2019
- http://www.indembkathmandu.gov.in/page/about-trade-and-commerce/, Accessed September, 13, 2019
- https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/news/india-extends-rs-16-billion-aid-to-nepal-for-rebuilding-earthquake-hit-houses/article27764441.ece, Accessed September, 13, 2019
- https://www.mea.gov.in/Speeches-Statements.htm?dtl/30343/translation Accessed September, 14, 2019
- https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1528217, Accessed September, 16, 2019
- https://www.nrb.org.np/red/publications/study_reports/Study_Reports--A_Survey_Report_on_Foreign_Direct_Investment_in_Nepal).pdf, Appendix III, Pg no. 34, Accessed September, 15, 2019
- https://idsa.in/issuebrief/nepal-china-transit-agreement-nnayak-270918, Accessed September, 16, 2019
- https://mofa.gov.np/press-release-on-the-state-visit-of-rt-hon-president-to-china-day-6/, Accessed September, 16, 2019
- https://mofa.gov.np/press-release-on-the-visit-of-hon-minister-for-foreign-affairs-to-dalian-china-day-1/, Accessed September, 13, 2019
- https://mofa.gov.np/press-release-regarding-the-visit-of-chinese-foreign-minister/, Accessed September, 13, 2019
- https://thehimalayantimes.com/nepal/preparation-for-chinese-president-xi-jinpings-visit-has-begun-chinese-foreign-minister-wang-yi/, Accessed September, 16, 2019
- https://kathmandupost.com/national/2019/01/18/nepal-trims-projects-under-bri-from-35-to-9-at-chinese-call, Accessed September, 12, 2019
- https://southasianvoices.org/nepals-delicate-dance-with-china-on-bri/, Accessed September, 12, 2019
- https://www.thethirdpole.net/en/2019/06/18/china-nepal-railway-fantasy-or-reality/, Accessed September, 13, 2019
(The paper is the author’s individual scholastic articulation. The author certifies that the article/paper is original in content, unpublished and it has not been submitted for publication/web upload elsewhere, and that the facts and figures quoted are duly referenced, as needed, and are believed to be correct). (The paper does not necessarily represent the organisational stance... More >>
Image Source: https://www.narendramodi.in/gu/pm-modi-and-nepal-pm-jointly-inaugurate-petroleum-pipeline-between-amlekhgunj-and-motihari-546388









Post new comment